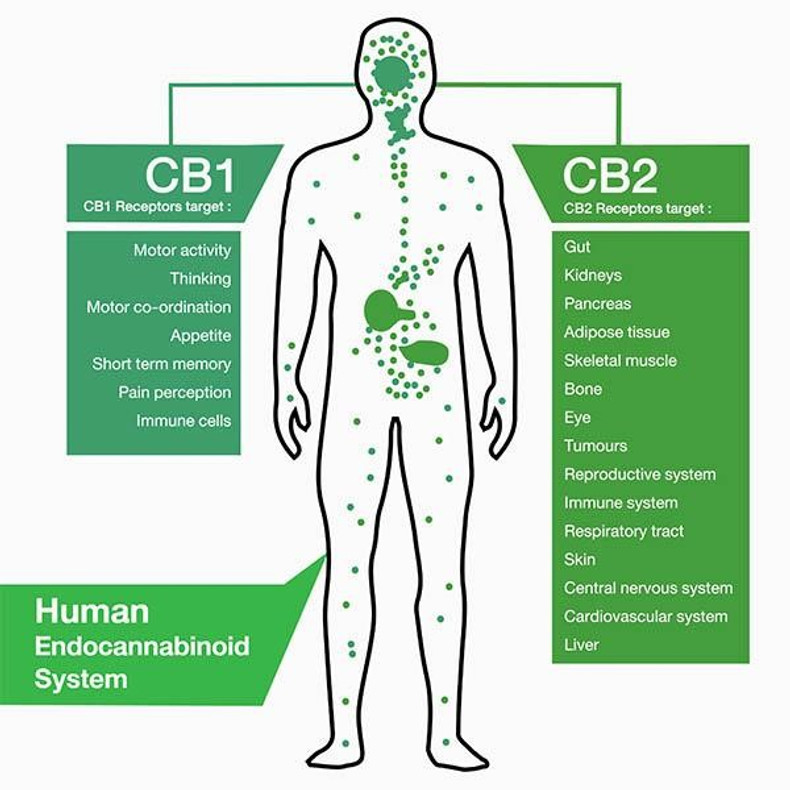
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex network of receptors, neurotransmitters, and enzymes that plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological and cognitive processes in the human body. This system is responsible for maintaining homeostasis, or balance, in the body, and helps regulate functions such as mood, appetite, sleep, pain, and immune system response.
The ECS consists of two main types of receptors, CB1 and CB2, that are found throughout the body. These receptors are activated by neurotransmitters called endocannabinoids, which are naturally produced by the body. Endocannabinoids, such as anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), bind to these receptors and trigger a response.
The active compounds in cannabis, known as cannabinoids, also interact with the ECS. The most well-known cannabinoid is delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is responsible for the plant's psychoactive effects. THC binds to the CB1 receptors in the brain, which can lead to changes in mood, perception, and cognitive function.
Another important cannabinoid is cannabidiol (CBD), which does not produce psychoactive effects. Instead, CBD has been shown to have a range of therapeutic effects, such as reducing anxiety and inflammation, and improving sleep and overall wellness. CBD is thought to interact with the ECS in several ways, including blocking the degradation of endocannabinoids and modulating the activity of CB1 and CB2 receptors.
In addition to these two main cannabinoids, cannabis contains over 100 other compounds that may also interact with the ECS. These compounds, known as terpenes, have their own unique effects and may enhance or modulate the effects of THC and CBD.
The ECS is thought to be a key component in the development of several medical conditions, including chronic pain, anxiety, and depression. By targeting the ECS, it is believed that cannabis and its derivatives could have therapeutic benefits for these conditions.
For example, the use of cannabis for pain management has been well documented, with studies showing that it can help reduce chronic pain and improve quality of life in patients with conditions such as fibromyalgia and multiple sclerosis. In addition, the anxiolytic effects of CBD have been demonstrated in several clinical trials, suggesting that it may be an effective treatment for anxiety disorders.
In conclusion, the endocannabinoid system is a complex and dynamic system that plays a crucial role in maintaining balance in the body. The interaction of cannabis and its derivatives with the ECS has the potential to offer therapeutic benefits for a range of medical conditions, and is an area of ongoing research. As the science behind the ECS and its interaction with cannabis continues to evolve, it is likely that new and innovative treatments will emerge in the future.